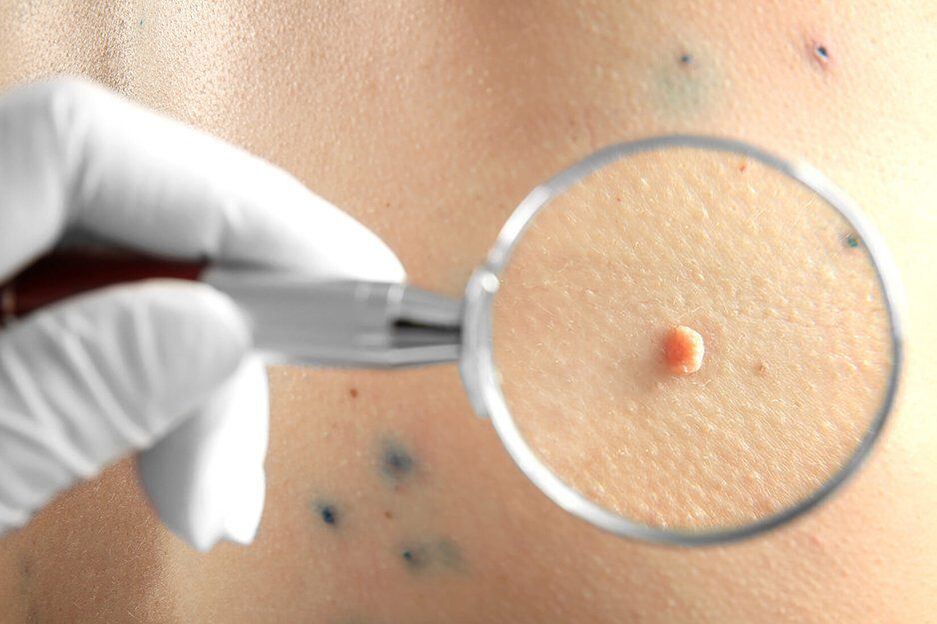
Papillomas are common in modern society. According to medical statistics, they are seen in one form or another in 80% of people and are small benign tumor-like formations in the skin and mucous membranes of different parts of the body. They are just one of the manifestations of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, whose strains are over 190 species. Among them, the viruses with high, medium and low oncogenic risk stand out. Therefore, in addition to an aesthetic disadvantage, papillomas can pose a serious danger to life and human health, as some of them can turn into malignant tumors.
What is HPV
The human papillomavirus infects only humans and its main route of transmission is sexual. Therefore, HPV is more common among sexually active people. This explains the fact that most often the infection occurs at a young age, at the time of onset of sexual activity and at its peak, ie, 15-25 years. In addition, several strains (types) of HPV can be simultaneously in the human body, causing the appearance of different types of tumor formations in the skin and mucous membranes.
The disease caused by HPV is called papillomatosis.
Infection with the virus occurs when it comes in contact with the skin or mucous membranes with skin particles or mucous membranes from an infected person. They attach to the membranes of immature epithelial cells, from where they penetrate into the cell's cytoplasm and later into the nucleus. It is in the nucleus of the cell that the DNA is, which HPV damages. As a result, when the affected cell divides, the consequence will be the formation of new, unhealthy cells, but with altered genetic information, which leads to disruptions in the mechanism of their reproduction and differentiation. This becomes the reason for the appearance of neoplasms in the skin and mucous membranes.
HPV infection can lead not only to the formation of papillomas, but also warts, as well as flat and genital warts. However, it can be asymptomatic. In this case, the patient will not show outward signs of human papillomavirus infection, but will act as a carrier and may infect others during unprotected sex or at home.
Thus, HPV infection does not always lead to papilloma formation. It depends on the strength of the person's immunity, but most often the first small papillomas appear 1 to 6 months after infection.
The human papillomavirus is intracellular. Therefore, with sufficient strength of the immune system, the body successfully suppresses its activity and does not offer the opportunity to trigger cell proliferation. But with the weakening of immunity due to the action of some factors, the body's defenses fall, the virus is activated, which leads to the formation of papillomas.
All strains or types of HPV can be divided into 4 groups:
- non-oncogenic - strains 1-5, 63;
- low oncogenic risk - strains 6, 11, 40, 42-44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81;
- medium oncogenic risk - strains 26, 31, 33, 35, 51-53, 58, 66;
- high oncogenic risk - strains 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 59, 68, 73, 82 (types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous).
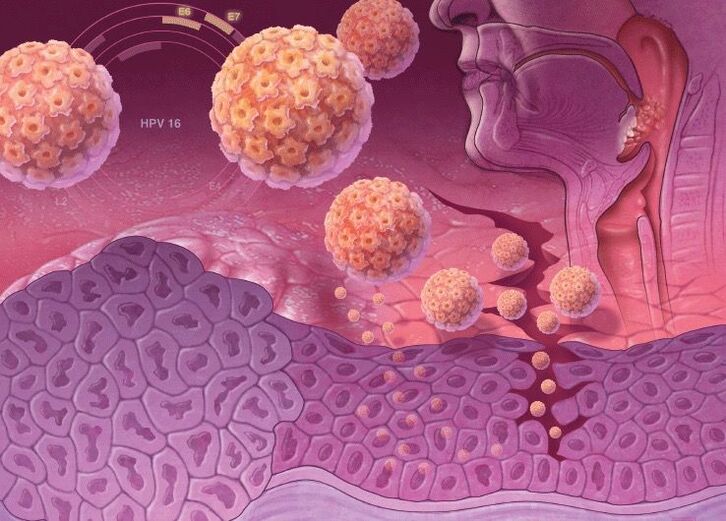
High oncogenic risk HPV strains have special genes in their DNA that are responsible for the synthesis of specific proteins, oncoproteins (E6 and E7). Therefore, when it is incorporated into the DNA of a human cell, its anti-cancer protection diminishes. Oncoproteins destabilize the skin cell genome, cause its active reproduction and suppress the ability to differentiate. Therefore, this is fraught with a high risk of developing cancer when infected with high-risk oncogenic strains of human papillomavirus.
The magnitude of the danger posed by papillomas depends directly on the HPV type. Infection with strains with high oncogenic risk is dangerous for development:
- cervical cancer;
- malignant tumors of the anus, vulva, penis;
- oropharyngeal cancer, etc.
70% of cervical cancer cases are due to HPV types 16 and 18 infection.
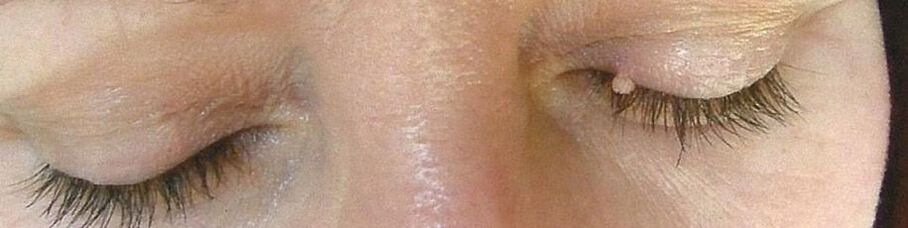
But even when infected with low-risk oncogenic strains with papilloma formation, they should be treated with caution. Convex neoplasms are usually damaged by clothing, bleed and tend to become inflamed. At the same time, perhaps the greatest discomfort is caused by the formations in Organs genitals, which cause great discomfort and make it difficult to lead an intimate life. In such cases, it is possible to attach a secondary infection, which can cause the development of septic-purulent complications. In addition, papillomas can form on the mucous membranes of almost any internal organ, which leads to their work being interrupted. Therefore, papillomatosis of the upper respiratory tract is often found, which causes difficulty in breathing.
Causes of papilloma formation and risk factors
HPV can be transmitted sexually as well as from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. The virus transmission via household contact is not excluded, that is, with the combined use of towels, clothes, etc. This explains the high prevalence of HPV worldwide. Autoinfection is also possible. In that case, if a papilloma is injured, the virus can be transferred to healthy areas of the skin and affect them.
The main causes of HPV infection are frequent changes of sexual partner and unprotected sex.

But infection with a virus does not always lead to the formation of papillomas, genital warts, and so on. The probability of developing papillomatosis depends on several factors:
- immunodeficiency of any origin, including the use of drugs that suppress immunity (immunosuppressants, cytostatics, etc. ), the presence of HIV infection, radiation damage;
- decreased body defenses in the context of physiological changes during pregnancy;
- early onset of sexual activity, when the immune system is not fully formed and strengthened;
- microtrauma of the skin and mucous membranes;
- infection with highly oncogenic HPV strains;
- the presence in the body at the same time of several types of HPV;
- the presence of other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), in particular gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B and C, etc. ;
- hormonal disorders;
- body exhaustion, hypovitaminosis, chronic fatigue and severe stress;
- multiple births and abortions;
- the presence of serious chronic diseases, in particular diabetes mellitus;
- lead an unhealthy lifestyle, the presence of bad habits;
- poor living conditions.
Elderly and overweight people are more prone to papilloma formation. In addition, their neoplasms often form in the skin folds, which contributes to their damage and inflammation.
Types and Symptoms
Neoplasms caused by HPV infection can form in the skin and mucous membranes of various parts of the body, including the face, neck, and décolleté. They can also form on the arms, legs, back, genitals, including the perineum, labia minora and majora, vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, especially along the coronal sulcus and frenulum. Damage to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, esophagus, bladder, eye conjunctiva, trachea and other internal organs is not excluded.
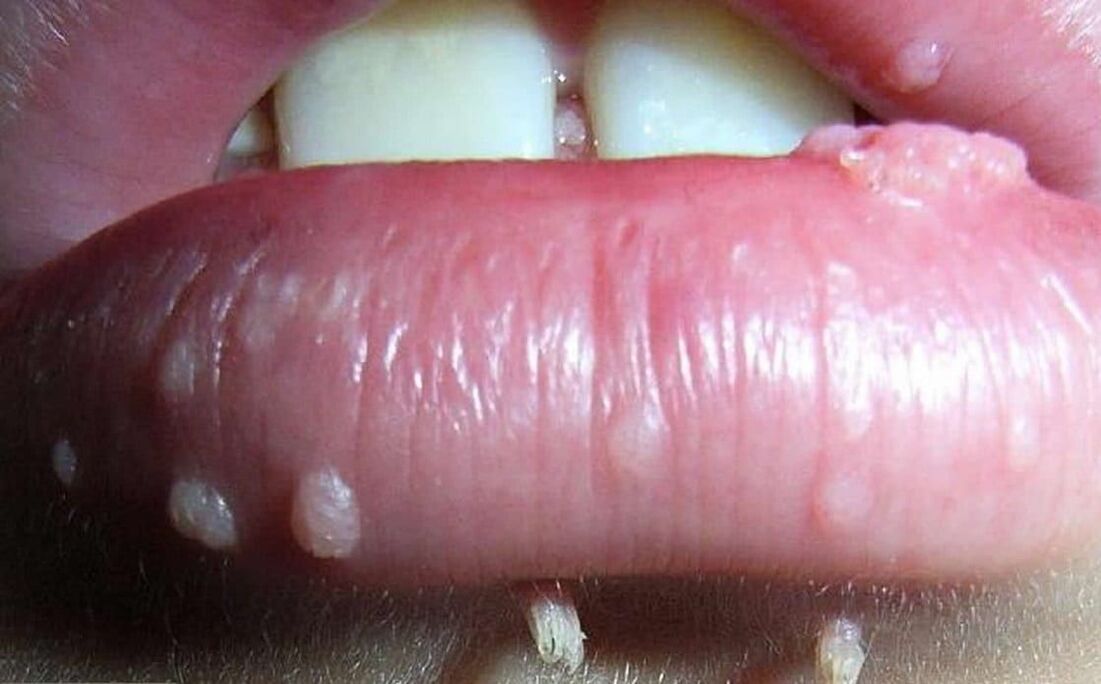
The human papillomavirus can lead to the appearance of neoplasms of different natures. In general, they can be divided into 3 groups, although in all cases the reason for their appearance is the same - human papillomavirus infection.
- Papillomas are pink, white, pearlescent or light brown benign neoplasms, forming most frequently on the eyelids, lips, chest, armpits and neck. They are located alone and generally do not tend to fuse, even with multiple injuries. Papillomas are usually round or bumpy, resemble the head of a cauliflower, most often have a leg.
- Warts are benign, dirty-brown or paler formations in the shape of a cock's comb or a cluster of villi held together by a common base. They are most often found in the genital area, anus and around the mouth. They tend to fuse together and, as a result, cover large areas of the body. Its appearance is due to infection with HPV types 6 and 11. Distinguish between sharp, flat, and intraepithelial warts.
- Warts are irregular, light, benign tumor-like formations in the form of a plaque or a small nodule on the skin surface of the hands, nails, feet, face, and front of the body. Warts may look like papillomas but differ from them on a broad basis. They usually occur with HPV infection of 1-5, 7-10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-24 types.
These tumor-like formations can range in size from a few millimeters to large growths that cover large areas of skin or mucous membranes.
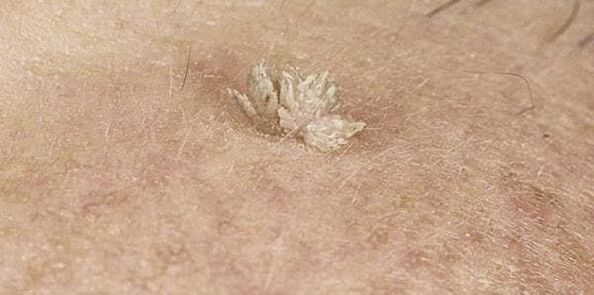
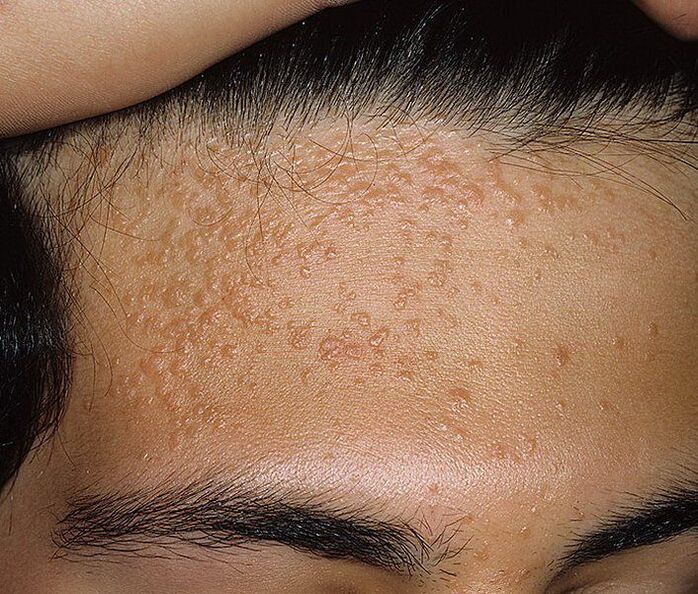
Also, neoplasms can have a different appearance, which directly depends on the type of HPV that has entered the body. More often than not, there are:
- Common or common - lumps of dense consistency with a diameter greater than 1 mm. They tend to merge and group together.
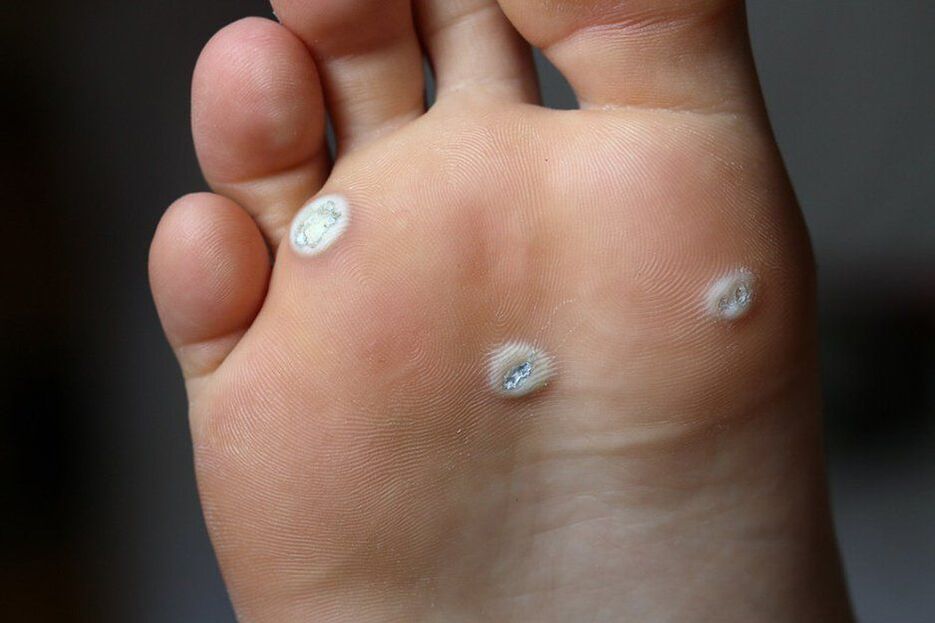
- Plantar warts appear above the surface of the skin, usually in painful bumps with a shiny surface and edge. One feature is the absence of a skin pattern. Its formation is caused by HPV types 1, 2, 4.
- Flat papillomas are smooth, smooth, flat, usually rounded growths that are normal skin color or slightly yellowish, pinkish. They can be itchy and so are often sore, sore, and inflamed. The causes of its formation are strains 3 and 10 of HPV.
- Filiforms (acrocords) are one of the most common papillomas, especially in elderly patients. Most often found in the face, around the eyes, in the groin, in the armpits, in the neck. They are yellowish in color and tend to grow gradually, turning into lumps of dense but elastic consistency.
- Genital warts on the perineum, genitals.
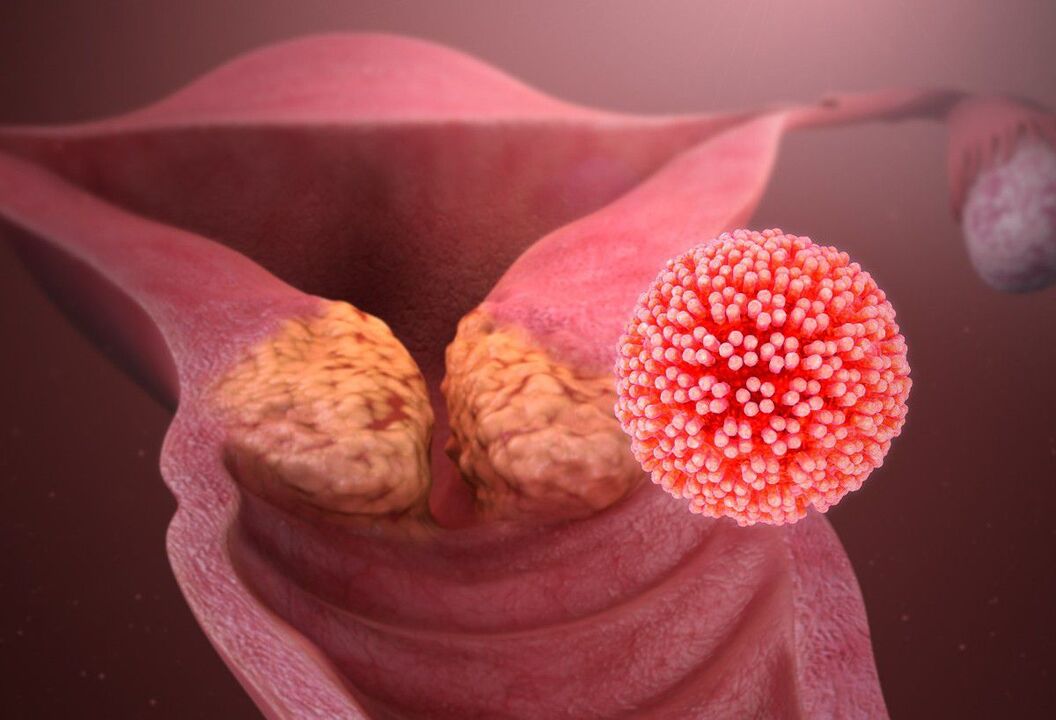
Papillomas can be visible to the naked eye or located in the thickness of the skin or mucous membranes. In the latter case, they are called endophytic and one of their manifestations is cervical dysplasia. Defeat of the female internal genitals by papillomatosis may indicate:
- itching, burning, crying in the perineum;
- profuse leukorrhea;
- secretion with blood, in particular, arising after intercourse;
- discomfort during intimacy.
Papillomatosis can sometimes cause back and pelvic pain, weakness, leg swelling, and unnecessary weight loss. These signs are among the most alarming, as they may indicate the development of complications from HPV infection.
Diagnosis
If papillomas form on the body, face, or genitals, you should consult a dermatologist. This will make it possible not only to diagnose human papillomavirus infection in the early stages, but also to take measures to prevent the formation of new elements, as well as to observe changes in existing ones.
It is especially important not to hesitate to visit a doctor if signs of growth, papilloma discoloration, unpleasant odor, or pain in the localized area appear.
First, the doctor will perform a dermoscopy, that is, an examination of the neoplasms with a special augmentation device. This will allow you to determine its nature, as well as notice dangerous signs that indicate a high probability of degeneration from a benign to a malignant formation, not to mention a formed cancer. If detected at an early stage of development, they are successfully treatable and have a favorable prognosis in the future.
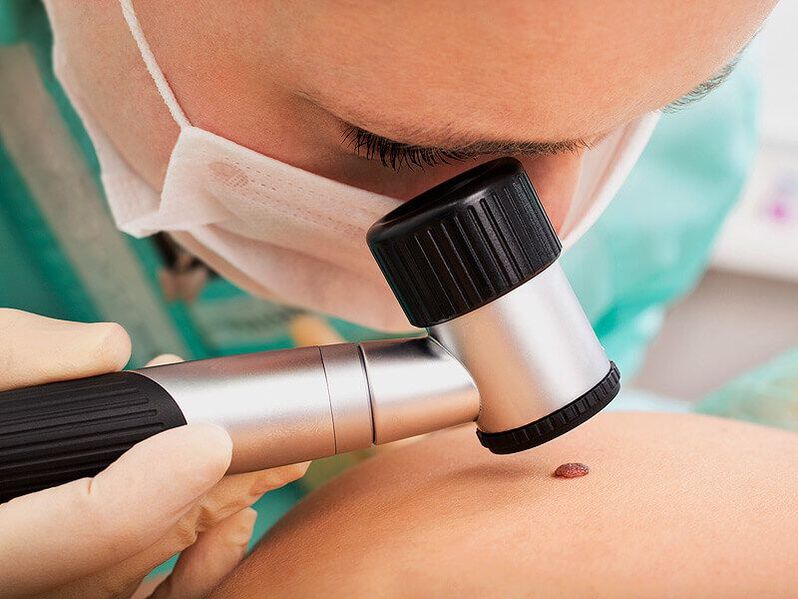
It is imperative that patients are tested for STDs, especially if warts are found in the genital area. Furthermore, in such situations, women receive advice from a gynecologist and men - from a urologist. This is important for diagnosing the presence of a human papillomavirus lesion in the cervix, urethra, etc. and, if necessary, prescribe the appropriate treatment.
To confirm papillomatous infection, patients usually undergo a PCR analysis. With their help, it is possible not only to confirm or deny human papillomavirus infection, but also to accurately determine the strains.
Treatment and removal of papillomas
The treatment of human papillomavirus infection is always complex. Of course, you can simply remove the disturbing papilloma, but in this case there is a high risk that soon a new one or even several will form in its place. As the main reason for the formation of papillomas is the decrease of the body's own defenses, which allows the dormant HPV in the body to become active, drug therapy is prescribed in the first place for patients with papillomatosis. Includes immunomodulators and antiviral agents. In extensive lesions of skin and mucous membranes with papillomas, cytotoxic drugs may also be prescribed. But they are taken under a doctor's supervision as they can cause serious side effects.
If a patient is diagnosed with concomitant infections or illnesses, appropriate treatment for the situation should be prescribed, and sometimes it is necessary to consult a specialist specialist and undergo therapy under their supervision.

All types of warts are subject to mandatory removal, as are papillomas, which are often sore and inflamed. In other cases, removal is carried out at the patient's request. But it is possible to begin to eliminate the visible manifestations of HPV infection only after the end of treatment of concomitant diseases, if any, and in the context of continued antiviral therapy.
In general, all modern methods of destroying or removing papillomas can be divided into 2 broad groups:
- chemical - consists of the use of various chemical compounds for the removal of papillomas, including trichloroacetic acid, dermatological preparations;
- physical - involves the removal of papillomas by surgery, through electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser, radio waves or plasma coagulation.
After the papilloma has been removed by one method or another, it is important to use topical agents prescribed by your doctor to speed healing and eliminate the risk of infection.
The success of the treatment and especially the removal of papillomas depends on the strength of the immune system. In its normal state, in 90% of cases, within 2 years from the time of infection, HPV is suppressed or even completely destroyed. But this is no guarantee that there is no risk of reinfection or the formation of new papillomas. If immunity is reduced due to the action of certain factors, papillomatosis becomes chronic, periodically relapses and can lead to serious complications.
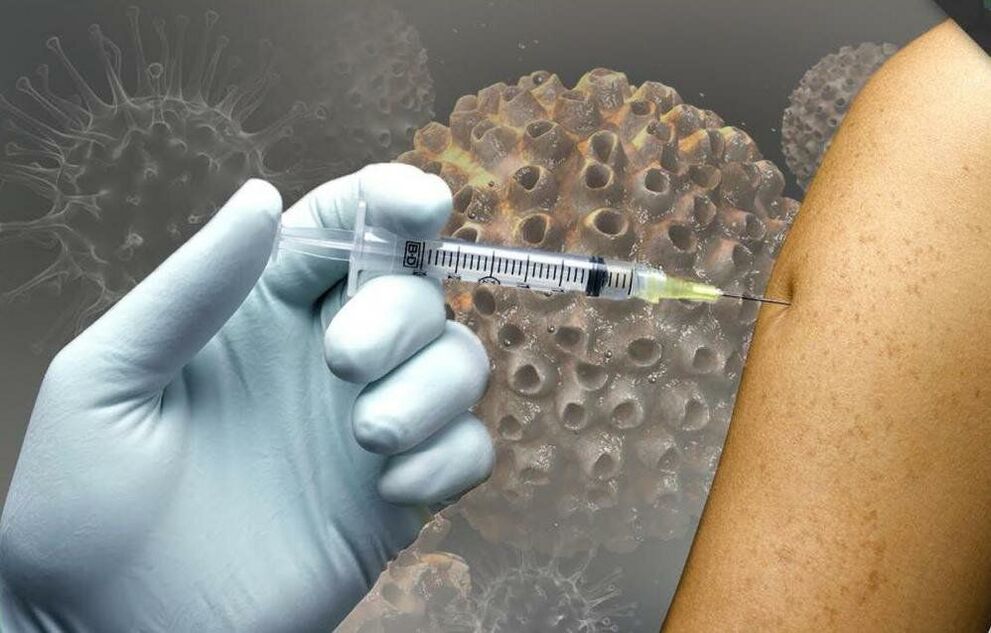
In order to prevent infection with dangerous HPV strains and the development of serious complications, it is recommended, especially for girls, to be vaccinated between 9 and 25 years of age.
Surgical removal of papillomas
The essence of the method is to remove the neoplasm with a scalpel, which is associated with scarring and increased healing time. Therefore, it is only used when it is necessary to remove a large papilloma or in those cases in which a histological examination is necessary, since malignant cells are presumed to form in it.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, which makes it painless. The doctor removes the neoplasm itself with a scalpel and captures the surrounding healthy tissue. This is necessary to eliminate the risk of papilloma re-formation in the same location. If it has a leg, it is dissected with surgical scissors and, with the aid of an electrocoagulator, the vessel that fed the neoplasm is "sealed". The remaining wound is sutured, treated with antiseptic and covered with a sterile dressing.
Today, surgical removal of papillomas is performed mainly when cancer cells are suspected.
cryodestruction
The method involves using low temperatures to destroy papilloma cells. This is accomplished through the use of liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which is -196 °C. The essence of the procedure is to use a special nipple or touch the papilloma with a cotton swab dipped in liquid nitrogen. Under its action, the water contained in the cells instantly transforms into ice crystals, which destroy them from within. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia or without it, as the exposure time to liquid nitrogen does not exceed 5-20 seconds.
The method's complexity lies in choosing the correct exposure time, in order to remove the papilloma in all its depth and not harm healthy tissues, which will lead to scar formation.
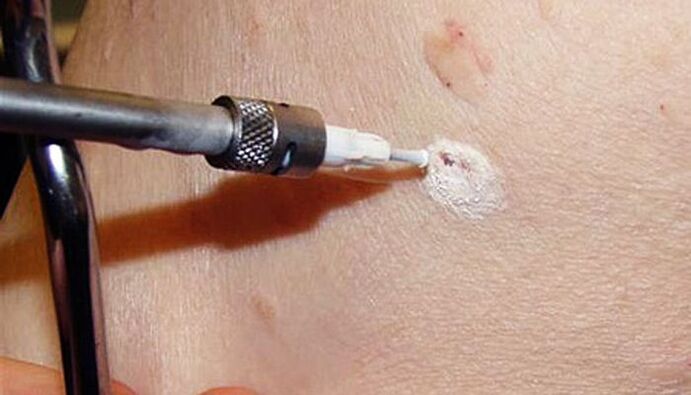
Immediately after treatment with liquid nitrogen, a white spot forms at the papilloma site. Later, a small blister with a clear or pinkish liquid content forms, and the surrounding skin becomes red and may swell a little. This may be accompanied by slight discomfort in the form of a burning or tingling sensation.
After 3-4 days, the blister bursts and a scab forms in its place, which disappears after a few days, exposing healthy, youthful skin. In no case should you independently pierce the bladder, injure it or otherwise injure the scab.
The cauterization of papillomas with liquid nitrogen is only possible in cases where the possibility of malignant cell formation in its interior is totally excluded. This method is most often used to remove genital papillomas and warts in:
- centuries;
- face;
- small joints;
- genitals.
Removal of papillomas with laser
Using a laser to remove papillomas is also possible only in cases where their malignancy is completely ruled out. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and consists of evaporating moisture from the papilloma cells with the thermal energy of a laser. Thus, a focused laser beam is aimed at the neoplasm. Duration of exposure does not exceed 1 minute.
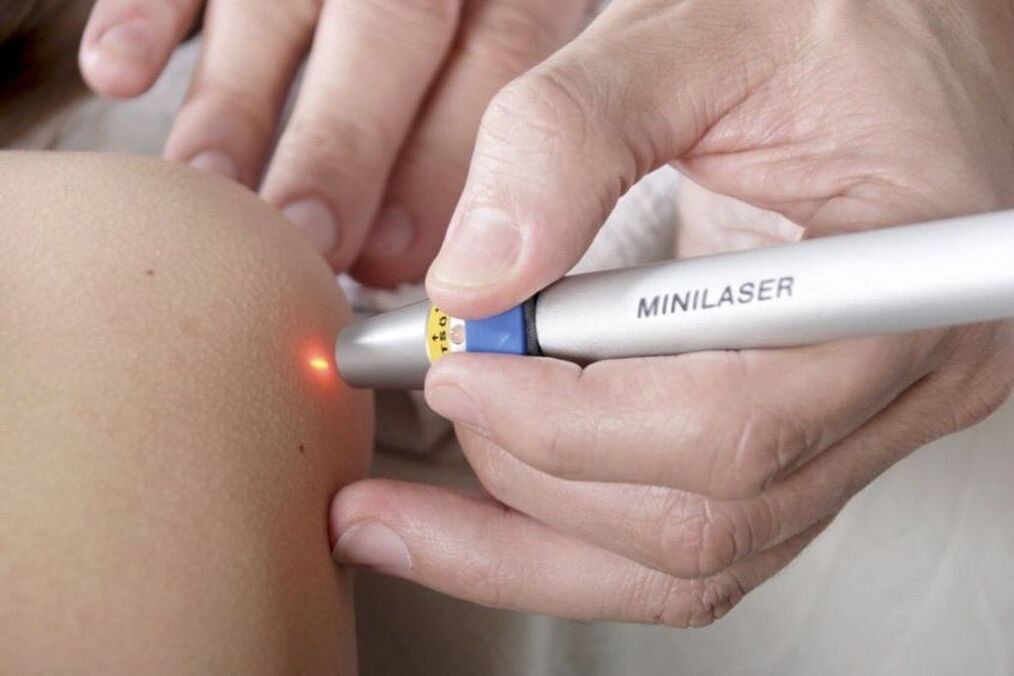
As a result, a scab forms at the papilloma site, and the surrounding skin becomes red and swollen. The crust will go away on its own in a week. It cannot be soaked and steamed for 3 days, as well as pulled out and bruised as it is full of scars. Also, within 2 weeks of removing the papilloma, it pays to protect the treated area from sunlight. Otherwise, there is a high probability of hyperpigmentation in this area.
When removing papillomas from the face with a laser, do not apply decorative cosmetics to the affected area until completely cured.
After the crust has fallen off, healthy pink skin is exposed, which gradually takes on a normal tone. This is the main advantage of laser removal of papillomas as it does not involve scarring and scarring. They can form only when large neoplasms are removed and post-operative care rules are violated. Furthermore, laser removal completely eliminates the risk of wound infection and is an absolutely bloodless method, since under the influence of thermal energy the instantaneous coagulation of small blood vessels occurs.
With the help of a laser, papillomas are removed mainly in:
- hands;
- legs and feet;
- face;
- centuries;
- neck;
- genitals.
Laser is the only reliable way to remove plantar warts, as their roots can penetrate 1 cm or more into the tissue.
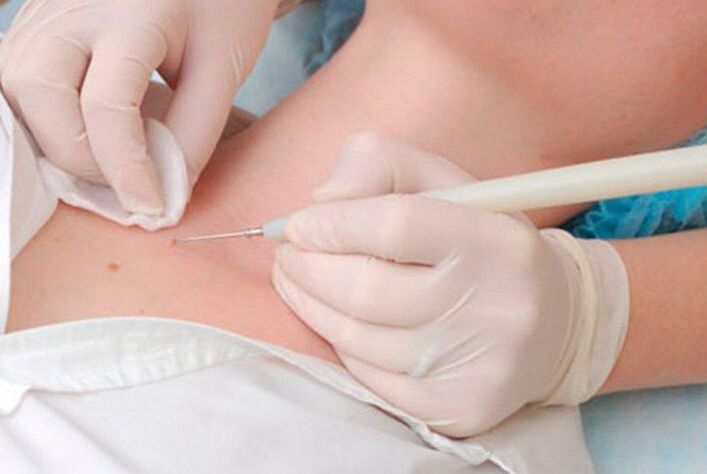
Papilloma electrocoagulation
The essence of the method is to use an electric current to remove the papillomas. Using a special device called an electrocoagulator, the doctor captures the papilloma and cuts it into healthy tissue. In this case, bleeding is completely absent, as the thermal energy of the current is sufficient for the clotting of small blood vessels. But the procedure can be painful, especially if you need to remove growth from areas of the body with delicate skin.
After electrocoagulation, a scab also forms. And the entire recovery period takes 7-10 days. After the crust has fallen off, the skin under it must be protected from damage and exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The method is used to remove papillomas from different parts of the body. Furthermore, electrocoagulation can also be used in cases where it is necessary to perform a histological examination of a neoplasm and precisely establish its nature. But the outcome of the procedure depends entirely on the qualification and experience of the doctor, however, as in other cases, since if the removal is not deep enough, the papilloma can form again in the same area.
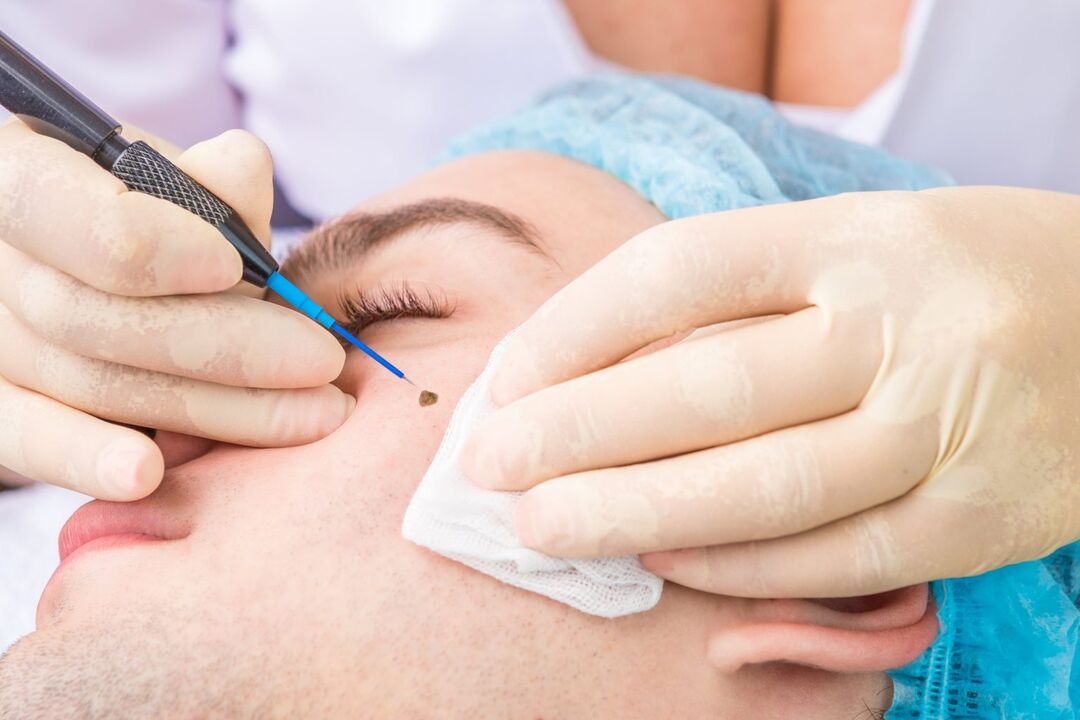
radio wave surgery
This method is one of the most advanced in removing papillomas of any type. It involves the use of a special device. But at the same time, it has a lot in common with laser papilloma removal. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and removal occurs directly due to exposure of the neoplasm to radio waves. Thanks to them, it is possible to completely cut the papilloma of any size and location, as well as avoid scarring.
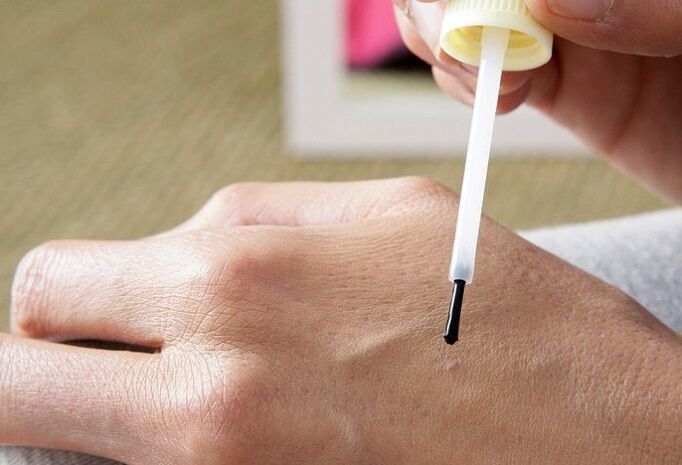
Chemical removal of papillomas
The method involves the regular application of special compounds to the papilloma, which destroy its cells, which leads to the subsequent disappearance of the neoplasm. But when using these medications, it is important to be very careful not to allow the substance to come into contact with healthy skin.
Thus, everyone can face papilloma formation. There is no effective prevention of HPV infection and vaccines only protect against the most dangerous strains of the virus in terms of cancer risk. However, in most cases, they do not cause significant inconvenience to the person, with the exception of genital and anus warts, which must be removed. In any case, you can get rid of any papilloma quickly and effectively, but as it is impossible to completely destroy the HPV in the body with medication and there is always the risk of becoming infected again or by another strain, there is a possibility that the problem will come back again. The only reliable way to minimize the likelihood of papilloma formation is to strengthen the immune system. And if they appear and represent a cosmetic defect or interfere in a person's daily life, look for a dermatologist. Your doctor will be able to accurately differentiate papillomas from other skin cancers and will resolve this issue in a matter of minutes.























